by
Vincy. Last modified on December 7th, 2021.
Integrating Stripe Apple pay into a web application is easy. It requires a few steps to achieve this integration. This article shows how to enable Apple or Google pay option using Stripe.
We can divide this article into 2 sections. It narrates the action items, prerequisites, and codes for the payment integration.
- Preparing your web environment to display the payment request option.
- Building PHP example for Stripe Apple Pay integration.
If you are new to the Stripe payment integration, check with the linked article. It explains how to get the Stripe API app credentials and other basic knowledge.
About Stripe Payment Request Button Element
This payment method collects details from customers using Stripe Apple Pay dialog. We have already seen how to collect recurring payments using Stripe subscriptions.
Stripe’s Payment Request Button method mounts a UI control to allow payment. This is a single point of integration for Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Microsoft Pay.
By ticking up the list of prerequisites in the documentation, we can see any one of the below buttons in the UI.

1. Preparing your web environment to display the payment request option
This section will tell the steps to display the Stripe apple pay. In Chrome or Microsoft edge, this will show other payment request buttons in a web interface.
- Ensure that the domain is HTTPS enabled.
- Let the domain pass through the Apple pay’s verification process.
- Save cards or other payment methods to the browser. The specifications vary based on the payment methods and browsers.
How to verify a domain with Apple Pay?
Follow the below steps to display the Stripe Apple pay button in your interface.
- Download and put the domain association file in the following path of your web root.
/.well-known/apple-developer-merchantid-domain-association.
- Request to create a Stripe Apple Pay domain. This can be done in any one of the below methods.
- By navigating to the Stripe Apple Pay tab in the Account Settings of your Dashboard.
- By using the API with your live secret key.
- Use API keys to make payments via the website registered with Apple Pay Stripe.
Note: Need not create Apple merchant id or generate certificate signing request (CSR). Stripe will take care of these in the back end.
API request to create Stripe Apple Pay domain
The following PHP script shows how to create a Stripe API.
\Stripe\Stripe::setApiKey("STRIPE SECRET KEY HERE"); \Stripe\ApplePayDomain::create([ 'domain_name' => 'example.com',
]);
2. Building PHP example for Stripe Apple pay integration
These are the steps to integrate Stripe Apple pay in a PHP web application. Some of the below are similar as we have seen in the Stripe payment gateway integration example.
- Download the Stripe API client.
- Configure Stripe API keys and tokens.
- Verify the payment request and mount the Stripe Apple pay button.
- Request and Confirm payment.
- Handle shipping/delivery address change events.
- Creating PHP endpoints to prepare and initiate Stripe API requests.
Download the Stripe client
Download PHP stripe API client and add up in the application dependency. This will be helpful to create AppleDomain and PaymentIntent objects via API.
It is available on Github. You can install this via composer also. The command to install the Stripe-PHP library is,
composer require stripe/stripe-php
Configure Stripe API keys and tokens
This is the web application config file. It includes the keys used to access the payment request API for Stripe Apple pay integration.
It also contains the web application root and the payment or order endpoint URLs. It defines Product details and shipping amount to build the payment request.
Common/config.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; class Config
{ const ROOT_PATH = "http://localhost/stripe-apple-pay"; /* Stripe API test keys */ const STRIPE_PUBLISHIABLE_KEY = ""; const STRIPE_SECRET_KEY = ""; const STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET = ""; const RETURN_URL = Config::ROOT_PATH . "/success.php"; /* PRODUCT CONFIGURATIONS BEGINS */ const PRODUCT_NAME = 'A6900 MirrorLess Camera'; const PRODUCT_IMAGE = Config::ROOT_PATH . '/images/camera.jpg'; const PRODUCT_PRICE = '289.61'; const CURRENCY = 'usd'; const US_SHIPPING = 7; const UK_SHIPPING = 12;
}
Verify the payment request and mount Stripe Apple pay button
The index.php is a landing page that contains the product tile. It has the container to mount the Stripe Apple pay button.
The HTML elements have the data attributes to have the payment configurations.
In imports the Stripe.js library and the payment.js file created for this example.
index.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; require_once __DIR__ . '/Common/Config.php';
?>
<html>
<title>Stripe Apple Pay integration</title>
<head>
<link href="assets/css/style.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body> <div class="phppot-container"> <h1>Stripe Apple Pay integration</h1> <div id="payment-box" data-pk="<?php echo Config::STRIPE_PUBLISHIABLE_KEY; ?>" data-return-url="<?php echo Config::RETURN_URL; ?>"> <input type="hidden" id="unit-price" value="<?php echo Config::PRODUCT_PRICE; ?>" /> <input type="hidden" id="product-label" value="<?php echo Config::PRODUCT_NAME; ?>" /> <input type="hidden" id="currency" value="<?php echo Config::CURRENCY; ?>" /> <input type="hidden" id="shipping-amount" value="<?php echo Config::US_SHIPPING; ?>" /> <img src="<?php echo Config::PRODUCT_IMAGE; ?>" /> <h4 class="txt-title"><?php echo Config::PRODUCT_NAME; ?></h4> <div class="txt-price">$<?php echo Config::PRODUCT_PRICE; ?></div> </div> <!-- Element target to render Stripe apple pay button --> <div id="payment-request-button"> <!-- A Stripe Element will be inserted here. --> </div> </div> <script src="https://js.stripe.com/v3/"></script> <script src="assets/js/payment.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
This is a partial code of the payment.js file. It shows the script required for rendering the Stripe Apple pay button into the UI. It builds the Stripe payment request object by using the following details.
- Customer details: name, email, address.
- Amount
- Currency
- Shipping details: amount, description.
The data for these details are from the config file. The payment form HTML contains hidden fields and data attributes to hold the config. This script uses the data attributes and hidden data to prepare the request.
After preparing the request body, it calls canMakePayment() to verify the paymentRequest object. Once verified, then it will render the Apple pay button in the UI.
assets/js/payment.js
var publishableKey = document.querySelector('#payment-box').dataset.pk;
var returnURL = document.querySelector('#payment-box').dataset.returnUrl;
var unitPrice = document.querySelector('#unit-price').value;
unitPrice = Math.round((unitPrice * 100));
var productLabel = document.querySelector('#product-label').value;
var currency = document.querySelector('#currency').value;
var shippingAmount = document.querySelector('#shipping-amount').value;
shippingAmount = Math.round((shippingAmount * 100)); var stripe = Stripe(publishableKey, { apiVersion: "2020-08-27",
});
var paymentRequest = stripe.paymentRequest({ country: 'US', currency: currency, total: { label: productLabel, amount: unitPrice, }, requestPayerName: true, requestPayerEmail: true, requestShipping: true, shippingOptions: [ { id: 'Default Shipping', label: 'Default Shipping', detail: '', amount: shippingAmount, }, ],
}); var elements = stripe.elements();
var prButton = elements.create('paymentRequestButton', { paymentRequest: paymentRequest,
}); // Verify payment parameters with the the Payment Request API.
paymentRequest.canMakePayment().then(function(result) { if (result) { prButton.mount('#payment-request-button'); } else { document.getElementById('payment-request-button').style.display = 'none'; }
});
Request and Confirm payment
This section contains the rest of the payment.js code. It creates paymentIntent object by clicking the ‘pay’ button on the payment overlay.
Once paymentIntent is created, the endpoint returns the client-secret-key. Then, the script calls stripe.confirmCardPayment with the reference of the client-secret-key.
assets/js/payment.js
paymentRequest.on('paymentmethod', function(ev) { //Create Stripe payment intent var requestParam = { email: ev.payerEmail, unitPrice: unitPrice, currency: currency, name: ev.payerName, address: ev.shippingAddress.addressLine[0], country: ev.shippingAddress.country, postalCode: ev.shippingAddress.postalCode, shippingPrice: ev.shippingOption.amount, }; var createOrderUrl = "ajax-endpoint/create-stripe-order.php"; fetch(createOrderUrl, { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify(requestParam) }).then(function(result) { return result.json(); }).then(function(data) { // Script to confirm payment stripe.confirmCardPayment( data.clientSecret, { payment_method: ev.paymentMethod.id }, { handleActions: false } ).then(function(confirmResult) { if (confirmResult.error) { // Report to the browser that the payment failed, prompting it to // re-show the payment interface, or show an error message and close // the payment interface. ev.complete('fail'); } else { // Report to the browser that the confirmation was successful, prompting // it to close the browser payment method collection interface. ev.complete('success'); // Check if the PaymentIntent requires any actions and if so let Stripe.js // handle the flow. If using an API version older than "2019-02-11" instead // instead check for: `paymentIntent.status === "requires_source_action"`. if (confirmResult.paymentIntent.status === "requires_action") { // Let Stripe.js handle the rest of the payment flow. stripe.confirmCardPayment(clientSecret).then(function(result) { if (result.error) { // The payment failed -- ask your customer for a new payment method. } else { // The payment has succeeded. window.location.replace(returnURL + "?orderno=" + data.orderHash); } }); } else { // The payment has succeeded. window.location.replace(returnURL + "?orderno=" + data.orderHash); } } }); });
});
Handle shipping/delivery address change events
This section deals with the shipping options on-change events. This code is applicable only if the payment object is enabled with shipping options.
It hits the PHP endpoint via AJAX and gets the JSON to change the shipping options. It passes the selected shipping address to the PHP.
assets/js/payment.js
paymentRequest.on('shippingaddresschange', function(ev) { // Perform server-side request to fetch shipping options fetch('ajax-endpoint/calculate-product-shipping.php', { method: "POST", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }, body: JSON.stringify({ adress: ev.shippingAddress }) }).then(function(response) { return response.json(); }).then(function(result) { ev.updateWith({ status: 'success', shippingOptions: result.shippingOptions, }); });
});
This is the PHP endpoint file that reads the shipping data sent via AJAX. It parses the shipping data and gets the country from it.
It uses an appropriate shipping amount from the config based on the country. You can include your additional shipping calculation here if needed.
It returns a JSON response with the shipping address and corresponding amount.
ajax-endpoint/calculate-product-shipping.php
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/../Common/Config.php'; $content = trim(file_get_contents("php://input")); $jsondecoded = json_decode($content, true);
$country = filter_var($jsondecoded["adress"]["country"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
if ($country == 'UK') { $shippingAmount = Config::UK_SHIPPING;
} else { $shippingAmount = Config::US_SHIPPING;
} $shippingOptions = array( "shippingOptions" => array( array( "id" => 'Edited shipping', 'label' => "Shipping Costs based on Country", 'detail' => $detail, 'amount' => $shippingAmount ) )
); echo json_encode($shippingOptions);
exit(); ?>
Creating PHP endpoints to prepare and initiate Stripe API requests
The below PHP files contains the server-side code that hits API. It reads the request body and creates a payment object on sending the Stripe apple pay request.
The StripeService.php file sets the API secret key to the Stripe object. It contains a function captureResponse() function that updates orders and payment entity.
Stripe calls the webhook endpoint as configured in the config.php. This endpoint reads Stripe response. Then, it invokes the captureResponse() function to update the database.
PHP AJAX endpoint to create order
ajax-endpoint/create-stripe-order.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; use Phppot\StripeService;
use Phppot\StripePayment;
require_once __DIR__ . '/../Common/Config.php'; $content = trim(file_get_contents("php://input")); $jsondecoded = json_decode($content, true); if (! empty($jsondecoded)) { require_once __DIR__ . "/../lib/StripeService.php"; $stripeService = new StripeService(); $email = filter_var($jsondecoded["email"], FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL); $name = filter_var($jsondecoded["name"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); $address = filter_var($jsondecoded["address"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); $country = filter_var($jsondecoded["country"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); $postalCode = filter_var($jsondecoded["postalCode"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); $notes = 'Stripe Apple Pay Payment'; $currency = filter_var($jsondecoded["currency"], FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING); $orderReferenceId = $stripeService->getToken(); $unitPrice = ($jsondecoded["unitPrice"] + $jsondecoded["shippingPrice"]); $orderStatus = "Pending"; $paymentType = "stripe"; $customerDetailsArray = array( "email" => $email, "name" => $name, "address" => $address, "country" => $country, "postalCode" => $postalCode ); $metaData = array( "email" => $email, "order_id" => $orderReferenceId ); require_once __DIR__ . '/../lib/StripePayment.php'; $stripePayment = new StripePayment(); $orderId = $stripePayment->insertOrder($orderReferenceId, $unitPrice, $currency, $orderStatus, $name, $email); $result = $stripeService->createPaymentIntent($orderReferenceId, $unitPrice, $currency, $email, $customerDetailsArray, $notes, $metaData); if (! empty($result) && $result["status"] == "error") { http_response_code(500); } $response = json_encode($result["response"]); echo $response; exit();
}
Stripe apple pay webhook endpoint
webhook-ep/capture-response.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; use Phppot\StriService; require_once __DIR__ . "/../lib/StripeService.php"; $stripeService = new StripeService(); $stripeService->captureResponse(); ?>
Stripe Service with request-response handlers
lib/StripeService.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; use Phppot\StripePayment;
use Stripe\Stripe;
use Stripe\WebhookEndpoint;
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php'; class StripeService
{ private $apiKey; private $webhookSecret; private $stripeService; function __construct() { require_once __DIR__ . '/../Common/Config.php'; $this->apiKey = Config::STRIPE_SECRET_KEY; $this->webhookSecret = Config::STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET; $this->stripeService = new Stripe(); $this->stripeService->setVerifySslCerts(false); } public function createPaymentIntent($orderReferenceId, $amount, $currency, $email, $customerDetailsArray, $notes, $metaData) { try { $this->stripeService->setApiKey($this->apiKey); $paymentIntent = \Stripe\PaymentIntent::create([ 'description' => $notes, 'shipping' => [ 'name' => $customerDetailsArray["name"], 'address' => [ 'line1' => $customerDetailsArray["address"], 'postal_code' => $customerDetailsArray["postalCode"], 'country' => $customerDetailsArray["country"] ] ], 'amount' => $amount, 'currency' => $currency, 'payment_method_types' => [ 'card' ], 'metadata' => $metaData ]); $output = array( "status" => "success", "response" => array( 'orderHash' => $orderReferenceId, 'clientSecret' => $paymentIntent->client_secret ) ); } catch (\Error $e) { $output = array( "status" => "error", "response" => $e->getMessage() ); } return $output; } public function captureResponse() { $payload = @file_get_contents('php://input'); $sig_header = $_SERVER['HTTP_STRIPE_SIGNATURE']; $event = null; try { $event = \Stripe\Webhook::constructEvent($payload, $sig_header, $this->webhookSecret); } catch (\UnexpectedValueException $e) { // Invalid payload http_response_code(400); exit(); } catch (\Stripe\Exception\SignatureVerificationException $e) { // Invalid signature http_response_code(400); exit(); } if (! empty($event)) { $eventType = $event->type; $orderReferenceId = $event->data->object->metadata->order_id; $paymentIntentId = $event->data->object->id; $amount = $event->data->object->amount; require_once __DIR__ . '/../lib/StripePayment.php'; $stripePayment = new StripePayment(); if ($eventType == "payment_intent.payment_failed") { $orderStatus = 'Payement Failure'; $paymentStatus = 'Unpaid'; $amount = $amount / 100; $stripePayment->updateOrder($paymentIntentId, $orderReferenceId, $orderStatus, $paymentStatus); $stripePayment->insertPaymentLog($orderReferenceId, $payload); } if ($eventType == "payment_intent.succeeded") { /* * Json values assign to php variables * */ $orderStatus = 'Completed'; $paymentStatus = 'Paid'; $amount = $amount / 100; $stripePayment->updateOrder($paymentIntentId, $orderReferenceId, $orderStatus, $paymentStatus); $stripePayment->insertPaymentLog($orderReferenceId, $payload); http_response_code(200); } } }
}
Updating orders and payments in database
lib/StripePayment.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; use Phppot\DataSource; class StripePayment
{ private $ds; function __construct() { require_once __DIR__ . "/../lib/DataSource.php"; $this->ds = new DataSource(); } public function insertOrder($orderReferenceId, $unitAmount, $currency, $orderStatus, $name, $email) { $orderAt = date("Y-m-d H:i:s"); $insertQuery = "INSERT INTO tbl_order(order_reference_id, amount, currency, order_at, order_status, billing_name, billing_email) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) "; $paramValue = array( $orderReferenceId, $unitAmount, $currency, $orderAt, $orderStatus, $name, $email ); $paramType = "sdssssss"; $insertId = $this->ds->insert($insertQuery, $paramType, $paramValue); return $insertId; } public function updateOrder($paymentIntentId, $orderReferenceId, $orderStatus, $paymentStatus) { $query = "UPDATE tbl_order SET stripe_payment_intent_id = ?, order_status = ?, payment_status = ? WHERE order_reference_id = ?"; $paramValue = array( $paymentIntentId, $orderStatus, $paymentStatus, $orderReferenceId ); $paramType = "ssss"; $this->ds->execute($query, $paramType, $paramValue); } public function insertPaymentLog($orderReferenceId, $response) { $insertQuery = "INSERT INTO tbl_stripe_payment_log(order_id, stripe_payment_response) VALUES (?, ?) "; $paramValue = array( $orderReferenceId, $response ); $paramType = "ss"; $this->ds->insert($insertQuery, $paramType, $paramValue); }
}
?>
Stripe Apple Pay Output
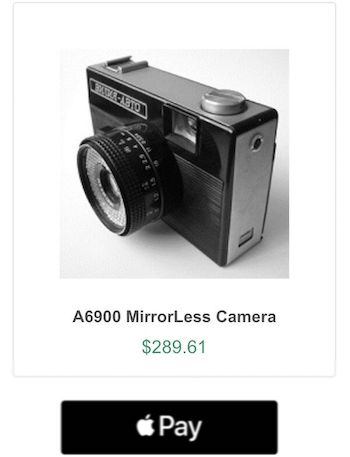
The below screenshot shows the product tile with the Stripe Apple pay button. The details are dynamic from the web application config.
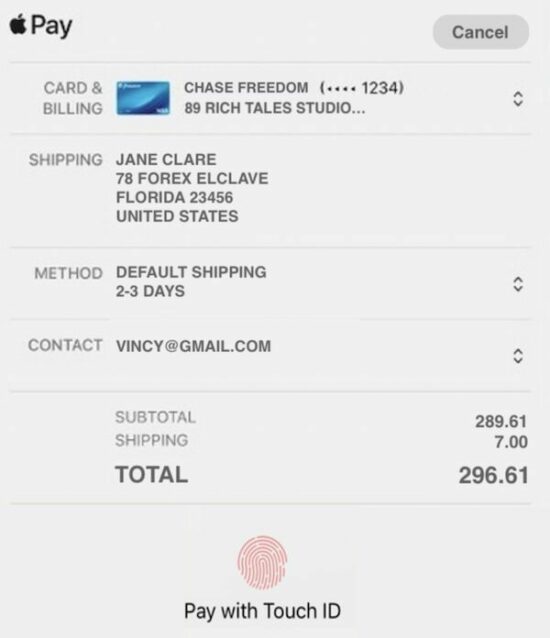
By clicking the Stripe Apple pay button in the above tile, the following payment dialog will pop up. It will have the option to proceed with payment by using the Apple touch id.
Conclusion
Thus, we have integrated Stripe Apple pay in a web application using PHP. We used the Stripe Payment Request Button to display the Apple pay option in the UI.
We have seen the pre-requisites and configuration steps needed for this integration. I hope, the example code helps to understand the steps easily.
Download
Popular Articles
↑ Back to Top