This is a running document in which I’ll answer all questions regarding the single line of Python code. If you want to check out my book “Python One-Liners” and become a one-liner wizard—be my guest! 
Let’s get started!
Python One Line If Without Else
Python One Line If Else
Python One Line Elif
Python One Line Function
Python One Line For Loop
Python One Line For Loop If
Python One Line For Loop Lambda
Python One Line While Loop
Python One Line HTTP Web Server
Want to create your own webserver in a single line of Python code? No problem, just use this command in your shell:

$ python -m http.server 8000
The terminal will tell you:
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000
To shut down your webserver, kill the Python program with CTRL+c.
This works if you’ve Python 3 installed on your system. To check your version, use the command python --version in your shell.
You can run this command in your Windows Powershell, Win Command Line, MacOS Terminal, or Linux Bash Script.
You can see in the screenshot that the server runs on your local host listening on port 8000 (the standard HTTP port to serve web requests).
Note: The IP address is NOT 0.0.0.0—this is an often-confused mistake by many readers. Instead, your webserver listens at your “local” IP address 127.0.0.1 on port 8000. Thus, only web requests issued on your computer will arrive at this port. The webserver is NOT visible to the outside world.
Python 2: To run the same simple webserver on Python 2, you need to use another command using SimpleHTTPServer instead of http:
$ python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8000
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 ...
If you want to start your webserver from within your Python script, no problem:
import http.server
import socketserver PORT = 8000 Handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler with socketserver.TCPServer(("", PORT), Handler) as httpd: print("serving at port", PORT) httpd.serve_forever()
You can execute this in our online Python browser (yes, you’re creating a local webserver in the browser—how cool is that)!
This code comes from the official Python documentation—feel free to read more if you’re interested in setting up the server (most of the code is relatively self-explanatory).
Source: Python One-Liner Webserver HTTP
Python One Line Webshell
Python One Line Write String to File
Python One Line Quine
Python One Line Quicksort
In this one-liner tutorial, you’ll learn about the popular sorting algorithm Quicksort. Surprisingly, a single line of Python code is all you need to write the Quicksort algorithm!
Problem: Given a list of numerical values (integer or float). Sort the list in a single line of Python code using the popular Quicksort algorithm!
Example: You have list [4, 2, 1, 42, 3]. You want to sort the list in ascending order to obtain the new list [1, 2, 3, 4, 42].
Short answer: The following one-liner solution sorts the list recursively using the Quicksort algorithm:
q = lambda l: q([x for x in l[1:] if x <= l[0]]) + [l[0]] + q([x for x in l if x > l[0]]) if l else []
You can try it yourself using the following interactive code shell:
Now, let’s dive into some details!
The following introduction is based on my new book “Python One-Liners” (Amazon Link) that teaches you the power of the single line of code (use it wisely)!

Introduction: Quicksort is not only a popular question in many code interviews – asked by Google, Facebook, and Amazon – but also a practical sorting algorithm that is fast, concise, and readable. Because of its beauty, you won’t find many introduction to algorithm classes which don’t discuss the Quicksort algorithm.
Overview: Quicksort sorts a list by recursively dividing the big problem (sorting the list) into smaller problems (sorting two smaller lists) and combining the solutions from the smaller problems in a way that it solves the big problem. In order to solve each smaller problem, the same strategy is used recursively: the smaller problems are divided into even smaller subproblems, solved separately, and combined. Because of this strategy, Quicksort belongs to the class of “Divide and Conquer” algorithms.
Algorithm: The main idea of Quicksort is to select a pivot element and then placing all elements that are larger or equal than the pivot element to the right and all elements that are smaller than the pivot element to the left. Now, you have divided the big problem of sorting the list into two smaller subproblems: sorting the right and the left partition of the list. What you do now is to repeat this procedure recursively until you obtain a list with zero elements. This list is already sorted, so the recursion terminates.
The following Figure shows the Quicksort algorithm in action:
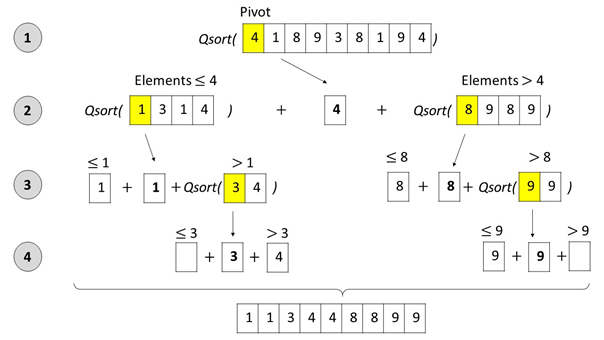
Figure: The Quicksort algorithm selects a pivot element, splits up the list into (i) an unsorted sublist with all elements that are smaller or equal than the pivot, and (ii) an unsorted sublist with all elements that are larger than the pivot. Next, the Quicksort algorithm is called recursively on the two unsorted sublists to sort them. As soon as the sublists contain maximally one element, they are sorted by definition – the recursion ends. At every recursion level, the three sublists (left, pivot, right) are concatenated before the resulting list is handed to the higher recursion level.
You create a function q which implements the Quicksort algorithm in a single line of Python code – and thus sorts any argument given as a list of integers.
## The Data
unsorted = [33, 2, 3, 45, 6, 54, 33] ## The One-Liner
q = lambda l: q([x for x in l[1:] if x <= l[0]]) + [l[0]] + q([x for x in l if x > l[0]]) if l else [] ## The Result
print(q(unsorted))
What is the output of this code?
## The Result
print(q(unsorted))
# [2, 3, 6, 33, 33, 45, 54]
Python One Line With Statement
Python One Line Exception Handling
Python One Line Try Except
Python One Line Execute
Python One Line Reverse Shell
Python One Line Read File
Python One Line Return If
Python One Line Regex Match
Python One Line Recursion
Python One Line Regex
Python One Line Read File to List
Python One Line Read Stdin
Python One Line Replace
Python One Line Ternary
Ternary (from Latin ternarius) is an adjective meaning “composed of three items”. (source) So, literally, the ternary operator in Python is composed of three operands.
Syntax: The three operands are written in an intuitive combination ... if ... else ....
<On True> if <Condition> else <On False>
| Operand | Description |
|---|---|
| <On True> | The return expression of the operator in case the condition evaluates to True |
| <Condition> | The condition that determines whether to return the <On True> or the <On False> branch. |
| <On False> | The return expression of the operator in case the condition evaluates to False |
Let’s have a look at a minimum example in our interactive code shell:
Exercise: Run the code and input your age. What’s the output? Run the code again and try to change the output!
Python One Line Two For Loops
Python One Line True False
Python One Line Too Long
Python One Line Two Commands
Python One Line To Multiple Line
Python One Line URL Decode
Python One Line Or
Python One Line Object
Python One Line Open File
Python One Line Print
Python One Line Print For Loop
Python One Line Print If
Python One Line Print List
Python One Line Parse JSON
Python One Line Pretty Print JSON
Python One Line Array Filter
Python One Line Append
Python One Line And Or
Python One Line Conditional Assignment
Python One Swap
Python One Line Sum
Python One Line Sort
Python One Line Semicolon
Python One Line Dictionary
Python One Line Function Definition
Python One Line Def
Python One Line Docstring
Python One Line Dict Comprehension
Python One Line Double For Loop
Python One Line Download File
Python One Line For Loop Append
Python One Line Generator
Python One Line FizzBuzz
Python One Line HTTP Get
Python Global in One Line
Python One Line Hello World
Python One Line Comment
Python One Line Class
Python Define Two Variables in One Line
Python Define Multiple Variables in One Line
Python One Line If (Not) None
Python One Line Map
https://www.sickgaming.net/blog/2020/07/...ne-line-x/


