In this one-liner tutorial, you’ll learn about the popular sorting algorithm Quicksort. Surprisingly, a single line of Python code is all you need to write the Quicksort algorithm!
Problem: Given a list of numerical values (integer or float). Sort the list in a single line of Python code using the popular Quicksort algorithm!
Example: You have list [4, 2, 1, 42, 3]. You want to sort the list in ascending order to obtain the new list [1, 2, 3, 4, 42].
Short answer: The following one-liner solution sorts the list recursively using the Quicksort algorithm:
q = lambda l: q([x for x in l[1:] if x <= l[0]]) + [l[0]] + q([x for x in l if x > l[0]]) if l else []
You can try it yourself using the following interactive code shell:
Now, let’s dive into some details!
A Conceptual Introduction
The following introduction is based on my new book “Python One-Liners” (Amazon Link) that teaches you the power of the single line of code (use it wisely)!

Introduction: Quicksort is not only a popular question in many code interviews – asked by Google, Facebook, and Amazon – but also a practical sorting algorithm that is fast, concise, and readable. Because of its beauty, you won’t find many introduction to algorithm classes which don’t discuss the Quicksort algorithm.
Overview: Quicksort sorts a list by recursively dividing the big problem (sorting the list) into smaller problems (sorting two smaller lists) and combining the solutions from the smaller problems in a way that it solves the big problem. In order to solve each smaller problem, the same strategy is used recursively: the smaller problems are divided into even smaller subproblems, solved separately, and combined. Because of this strategy, Quicksort belongs to the class of “Divide and Conquer” algorithms.
Algorithm: The main idea of Quicksort is to select a pivot element and then placing all elements that are larger or equal than the pivot element to the right and all elements that are smaller than the pivot element to the left. Now, you have divided the big problem of sorting the list into two smaller subproblems: sorting the right and the left partition of the list. What you do now is to repeat this procedure recursively until you obtain a list with zero elements. This list is already sorted, so the recursion terminates.
The following Figure shows the Quicksort algorithm in action:
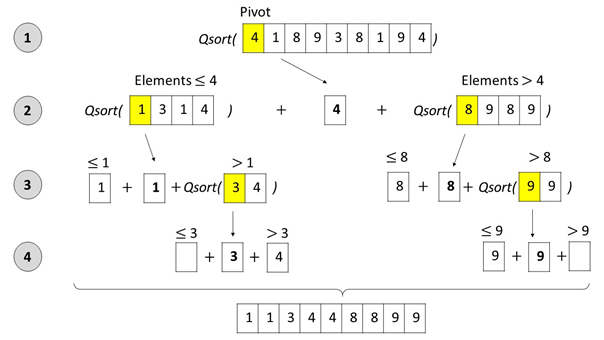
Figure: The Quicksort algorithm selects a pivot element, splits up the list into (i) an unsorted sublist with all elements that are smaller or equal than the pivot, and (ii) an unsorted sublist with all elements that are larger than the pivot. Next, the Quicksort algorithm is called recursively on the two unsorted sublists to sort them. As soon as the sublists contain maximally one element, they are sorted by definition – the recursion ends. At every recursion level, the three sublists (left, pivot, right) are concatenated before the resulting list is handed to the higher recursion level.
This brings us to the following code:
Python One-Liner Quicksort [Code]
Create a function q which implements the Quicksort algorithm in a single line of Python code – and thus sorts any argument given as a list of integers.
## The Data
unsorted = [33, 2, 3, 45, 6, 54, 33] ## The One-Liner
q = lambda l: q([x for x in l[1:] if x <= l[0]]) + [l[0]] + q([x for x in l if x > l[0]]) if l else [] ## The Result
print(q(unsorted))
Listing: One-liner solution for the Quicksort algorithm using recursion.
What is the output of this code? Let’s see…
Explanation Quicksort One-Liner
We have already discussed the recursive Quicksort algorithm above. The one-liner resembles exactly the discussed algorithm. First, we create a new lambda function q which takes only one list argument l.
The lambda function has the following structure:
lambda l: q(left) + pivot + q(right) if l else []
The lambda function returns the empty list [] in the recursion base case (that is – the list to be sorted is empty and, therefore, trivially sorted).
In any other case, it selects the pivot element as the first element of list l, divides all elements into two sublists (left and right) based on whether they are smaller or larger than the pivot. To achieve this, we use simple list comprehension.
As the two sublists are not necessarily sorted, we recursively execute the Quicksort algorithm on them. Finally, we combine all three lists and return the sorted list. Therefore, the result is:
## The Result
print(q(unsorted))
# [2, 3, 6, 33, 33, 45, 54]
Related: For an interactive experience of what you’ve just learned, check out our Instagram post about the Quicksort algorithm:
<script async="" src="//www.instagram.com/embed.js"></script>
Related Resources:
- The Shortest Quicksort Implementation
- Python One Line X
- Pythononeliners.com
- Book “Python One-Liners” (Amazon Link)
- Python One Line For Loop
- Python Quicksort One Line
Where to Go From Here?
Enough theory, let’s get some practice!
To become successful in coding, you need to get out there and solve real problems for real people. That’s how you can become a six-figure earner easily. And that’s how you polish the skills you really need in practice. After all, what’s the use of learning theory that nobody ever needs?
Practice projects is how you sharpen your saw in coding!
Do you want to become a code master by focusing on practical code projects that actually earn you money and solve problems for people?
Then become a Python freelance developer! It’s the best way of approaching the task of improving your Python skills—even if you are a complete beginner.
Join my free webinar “How to Build Your High-Income Skill Python” and watch how I grew my coding business online and how you can, too—from the comfort of your own home.
https://www.sickgaming.net/blog/2020/07/...quicksort/


